Superventas
Our products have demonstrated to be highly-effective in removing suspended particles and impurities from various types of wastewater.
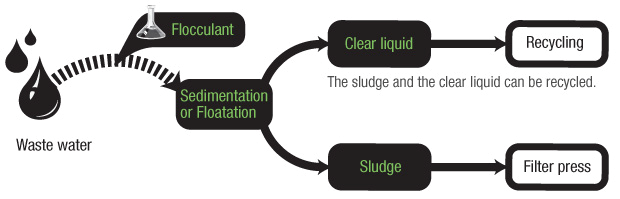
Polyacrylamide is a linear polymer comprised of monomers unit with functional groups of amide that adsorb on to the surface of particles. These particles are bridged together by the long polymer chain drawing the particles closer together. This process is called flocculation and is widely used in wastewater treatment.
PAM CHARACTERISTICS
|
FLOCCULATION |
PAM has the ability to bridge together particles suspended in solution by an adsorption process. Polymers often have electrostatic charges that allow for surface particle neutralization resulting in flocculation. |
|
ADSORPTION AND ADHESION |
PAM creates reversible covalent bonds between particle surfaces allowing the particle to gain size and mass. |
|
FRICTION REDUCTION |
PAM can effectively reduce fluid friction in a pipe. The friction loss can be minimized by 50-80% with small amounts of PAM added to a liquid. |
|
THICKENING |
PAM is used to thicken a variety of sludges in both neutral and acidic conditions. PAM used for thicken can have additional structures such as branched and cross-linked. PAM will hydrolyze at pH values above 10. |
When aqueous PAM solutions are mixed with sewage, the active amide groups on the polymer chain adsorb onto the surface of suspended material in the sewage and created bridges between them such that they now begin to exclude water from their newly formed structure. Once a small particle, now form larger flocs which can improve sedimentation rates in clarifiers, floatation rates in DAF systems and water removal in sludge thickening equipment. PAM is widely used in domestic sewage treatment, mining tailings pulp & paper making, petrochemicals, chemicals, textiles, oil sands and mining industries.
OUR PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
|
ITEMS |
ANIONIC PAM |
CATIONIC PAM |
NON-IONIC PAM |
AMPHOTERIC PAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PARTICLE SIZE (MM) |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
|
DRY WEIGHT (%) |
>89 |
>89 |
>89 |
>89 |
|
DISSOLUTION TIME (HOUR) |
<1 |
<1 |
<1 |
<1 |
|
INSOLUBLE (%) |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
|
MOLECULAR WEIGHT (MILLION) |
3-29 |
3-16 |
3-15 |
8-15 |
|
RELATIVE CHARGE (%) |
10-40 |
5-80 |
3-10 |
- |
|
ANIONIC CHARGE (%) |
- |
- |
- |
5-15 |
|
CATIONIC CHARGE (%) |
- |
- |
- |
5-50 |
|
RESIDUAL AM (PPM) |
<500 |
<500 |
<500 |
<500 |
|
PH RANGE |
5-14 |
2-14 |
3-10 |
1-14 |
APPLICATION
Anionic PAM: It is widely used in waste water treatment of chemical industry, municipal sewage treatment, such as coal washing, mineral processing, metallurgy, iron and steel industry and electronic industry. It is also used in oil industry to enhance oil recovery which is widely used. In addition, it can be used as paper additives and textile pulp agent.
Cationic PAM: It is very efficient in usage and has high dehydration rate. It is used for the waste water treatment in alcohol factory, monosodium glutamate factory, sugar factory, beverage factory, tanneries, dyeing and other fields. It has a better effect to be used together with inorganic coagulant in particular. It can be used as paper additives as well.
Non-ionic PAM: It is the most appropriate to use NPAM, when the sewage is acidic. It is also used as agents for the textile pulp, paper chemicals, water shutoff agent, and etc.Because of its non-ionic functional group, PH value and salts have a little influence on NPAM’s flocculation. In the neutral or alkaline conditions, the flocculation effect is not as good as APAM, but better than APAM in acidic conditions.
Amphoteric PAM: It can be used in a wide range of PH value. It can also be used in ore leaching with strong acid or extract valuable metals from the acid catalyst with metals. Amphoteric ion is not the mixing of anionic and cationic. It is applied to all kinds of waste water treatment like oil contamination, organic sewage, inorganic sewage, complex sewage with frequently water quality changing and sludge dewatering. It is also used as paper additives, oilfield water shutoff agent, and etc.


